4G fleet cameras are slowly becoming the industry norm. Nonetheless, one might ask – what’s the big deal with 4G fleet cameras? Are they that different from its predecessor?
Before answering that question, we’ll first discuss 3G, 4G, and LTE networks. Then, we’ll look at 4G fleet cameras against other fleet cameras.
3G, 4G & LTE Networks
Let’s forget about cameras for a second and talk about networks instead. What are 4G networks, and how are they different from 3G and LTE?
The short answer is they are all different wireless network generations. Each generation has its own procedures and protocols.
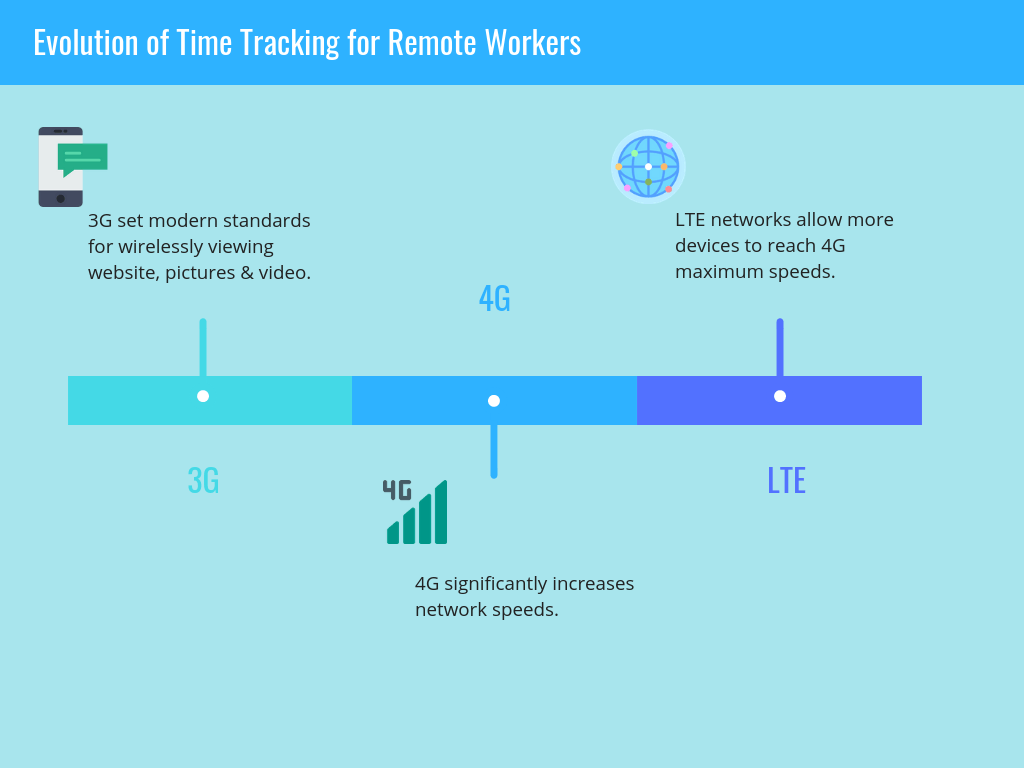
3G Networks
3G networks were revolutionary. It set standards for today’s wireless Internet because it allowed smartphone users to browse websites, view images, and watch videos.
4G Networks
Then, as people adapted to wireless Internet, they wanted more. Thus, 4G was born. 4G networks are much faster than 3G. In fact, some people get faster speeds on their smartphones than on their home Internet.
LTE Networks
Nonetheless, 4G Networks are not perfect. Devices react to 4G networks differently and experience different speeds. Thus, engineers created LTE, which is a form of 4G. LTE networks allow more devices to reach 4G’s maximum speed.
What does this mean for fleet users?
Ultimately, 4G fleet cameras mean two things.
Firstly, users experience faster Internet performance. For instance, it takes about 21 seconds to download a 30MB video file with 3G and about 5 seconds to download the same file on 4G.
Secondly, urban-area fleets are more likely to use 4G. As of right now, 4G is mainly available in urban areas whereas 3G is still the dominant network in rural areas.
In summary, these factors lead to the following outcomes:
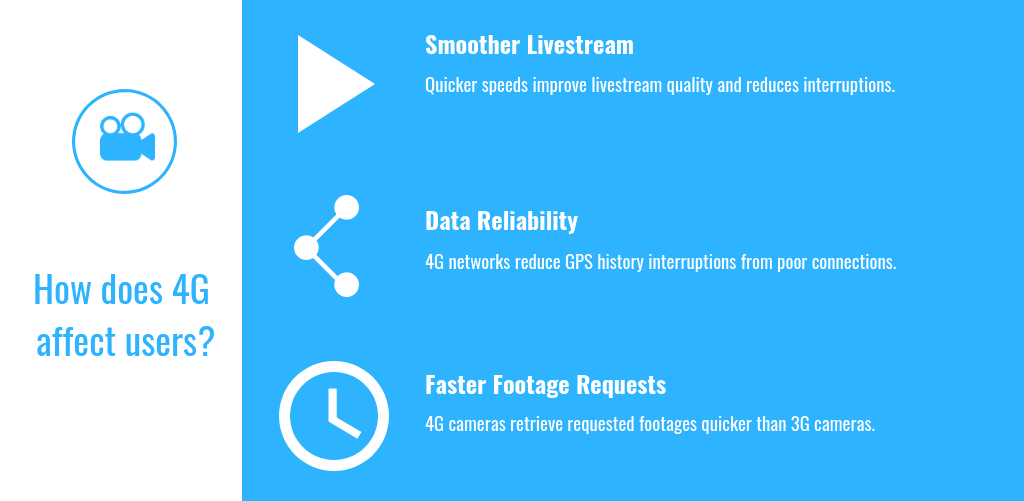
- Live streaming. Firstly, 4G fleet camera users experience smoother live streaming. In comparison, 3G fleet camera users may experience interruptions. It’s similar to browsing websites on 3G, where some sites and videos crash.
- Data reliability. Another advantage is getting more reliable data. Sometimes, 3G networks experience interruptions from poor connection. For instance, on a vehicle’s trip history, a user might see an interruption in the camera’s GPS breadcrumb. 4G networks reduce this occurrence.
- Faster footage request. Fleet camera users commonly retrieve recent footage. This is usually done by creating a footage request for a desired date and time. In turn, 4G camera networks retrieve footage faster than 3G camera networks.
DVR boxes are a great way to connect cameras onto a 4G network. Click here to view the CP4, one of our most common DVR boxes.
Links
WhistleOut: 3G vs 4G: What’s the difference?