If you’re in the service field, you probably heard of GIS Mapping Software. After all, some of the most well-known companies and organizations use some form of GIS Mapping Software.
What’s with the big buzz on GIS Mapping Software? In this post, we’ll explore what are GIS Maps, and who uses them.
What are GIS Maps?
GIS Maps, or “geographical info systems”, save, store and share maps with other users. In other words, people use GIS Mapping Software to overlap several pieces of data on a single map.
Let’s take a look at the history of GIS Maps in order to explain it. Before the 1900s, there was really only one type of map. That map is similar to what most people think a map should be – a document that shows roads and landmarks.
However, in the 20th century, people decided that maps do not have enough data. In the 1960s, a research group from Ottawa was doing a study on regional wildlife and decided to overlap things like wildlife landmarks and soil data on a map.
This idea went viral. Other people thought that it was a brilliant idea to overlap and share data on maps. Hence, GIS Maps was born.
Who Uses GIS Mapping Software?
Several organizations use GIS Mapping Software. Some examples include Winter Road Compliance, Electrical Service Providers, and Oil & Gas Management.
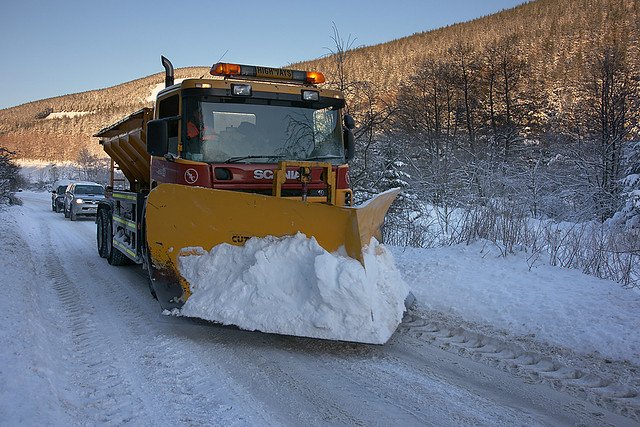
Winter Road Compliance
Winter road maintenance companies typically use GIS Maps for contract compliance. Hence, GIS Maps is a handy tool where users can upload and monitor winter road against contract terms.
Use case: City of Toronto
For instance, the City of Toronto has clear winter maintenance guidelines. The City website shares targets, such as clearing expressways within 2-3 hours of snowfall and clearing local roads within 14-16 hours of snowfall.
In this case, GIS Maps are useful because maintenance crews can plot contract roads onto a map. From there, operation managers can view the ground crew’s progress towards compliance targets and prioritize workers as necessary.
Electrical Service Providers
Another common user are electrical service providers. Electrical service providers have tons of electrical assets such as power lines and towers. In turn, electrical service crews greatly benefit by getting real time data like downed assets and nearby weather conditions.
Use case: CenterPoint Energy
CenterPoint Energy is a electrical and utility provider. They use the Esri ArcGIS program to track their electrical infrastructure.
Why is that important? Because CenterPoint serves millions of people across 6 states, they have thousands of electrical infrastructure. ArcGIS helps CenterPoint manage those thousands of assets by combining data onto a single map. As a result, electrical crews get real time data and provide faster service.
Oil & Gas Management
Our last example is in the oil and gas industry. One of the biggest challenges in the oil and gas industry is that a lot of their assets are underground or underwater pipes. Hence, GIS Maps plot these “hidden” assets onto a map.
Use case: BP Global
BP Global is one of the world’s leading oil and gas companies. They also use ArcGIS and had a project called “One Map”. The One Map Project involves using GIS Maps and creating a single map for every employee.
This is done by uploading data such as pipeline locations, environmental hazards, and even social conditions. As a result, BP employees were able to react faster to jobs and emergencies because they had unified, live data.
How do you integrate GIS Maps with Live Vehicle location? Read more on integrations here!