On November 7, Mike Millian, the president of the Private Motor Truck Council of Canada, released a notice stating that the use of electronic logging devices (ELDs) is a federal regulation that applies to all federally regulated carriers who are required to use logbooks, with some exemptions.
Because enforcement of this regulation for provincially-regulated carriers varies by province (as each province determines whether and when to enforce it), and due to the lengthy (and sometimes contradictory) rollout across North America, there has been some confusion as to what the ELD Mandate is, who it pertains to, and how to remain compliant.
General Information about the ELD Rule
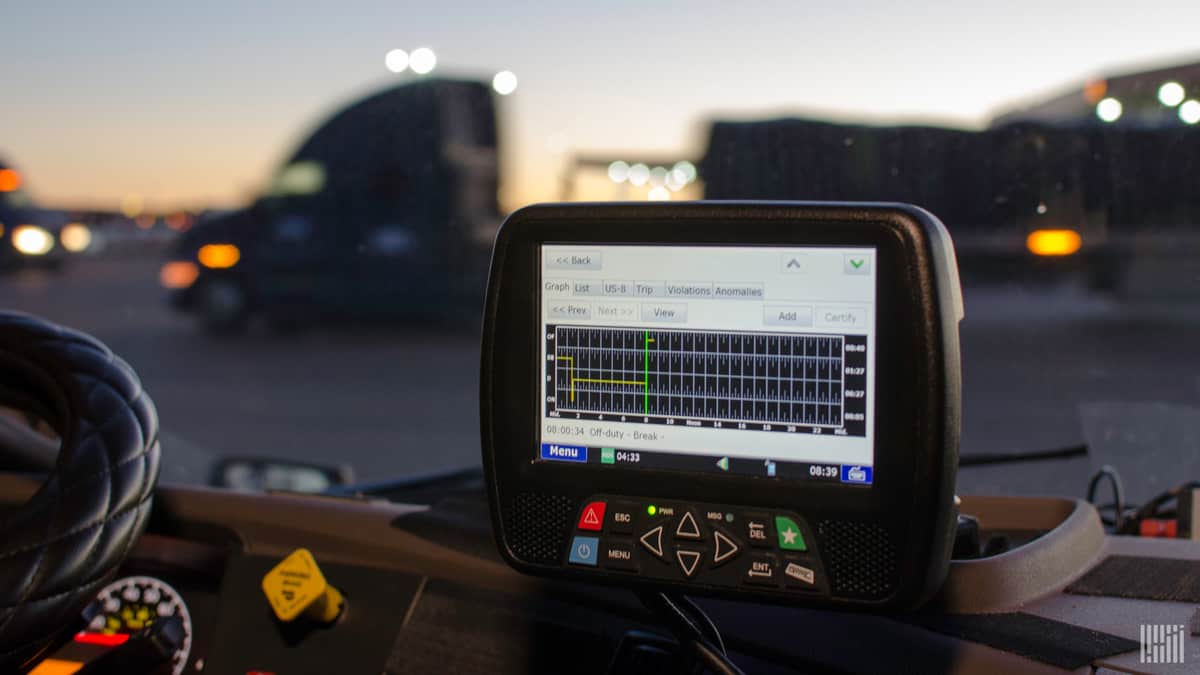
The ELD mandate was created to improve road safety and help reduce fatigue-related crashes among commercial motor vehicle operators. The rule requires most truck drivers and bus drivers to use ELDs, providing they are required to keep records of duty status (RODS) for more than 8 days in a 30-day period.
An ELD is used to record the time spent driving, on duty, not driving, and off duty. Drivers must also enter their RODS information into the ELD every 24 hours.
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) gave carriers two years after the effective date of the ruling, December 18th 2017, to comply with the ELD mandate. As of December 16th 2019, all ELDs had to be certified and installed in commercial motor vehicles, a ruling that has since extended to January 1, 2023.
The ELD mandate will help increase safety by monitoring drivers’ hours of service (HOS) more closely and providing carriers with up-to-date information regarding when a driver is approaching the maximum driving time allowed under federal law.
ELDs also provide real-time data that can be used to monitor a driver’s performance, identify any potential problems before they become serious issues, and reduce paperwork for owners and operators.
By moving to ELDs, carriers will be able to make sure their drivers are operating safely and staying in compliance with hours of service regulations. ELDs can also help streamline operations by providing up-to-date data that can be used to improve performance and reduce costs.
Overall, the ELD mandate is an important step towards improving safety on the roads and helping carriers operate more efficiently. By taking steps to become ELD compliant, carriers can ensure they are in compliance with federal law, avoid costly fines for noncompliance, and benefit from improved operational efficiency.
Is an ELD Mandatory?
Yes, an ELD is mandatory for all commercial motor vehicle drivers required to maintain records of duty status. According to the FMCSA, all such drivers must keep RODS from December 18, 2017 onward and use an ELD instead of paper logs or logging software.
It is important for drivers to be aware of these rules and comply with them properly. Failure to do so can result in penalties such as fines or lost driving privileges. Drivers who are found to be in violation could also face civil or criminal action. For carriers that do not comply with the ELD mandate, penalties can include warnings or out-of-service orders which can result in disruptions to operations and lost revenue.
In addition, many states have passed laws to enforce the federal mandate and make sure that truck drivers comply with it. It is important for drivers to be aware of all applicable rules in their area and follow them accordingly. By doing so, they can help ensure their safety as well as that of other road users.
How to Comply: Rules and Regulations
One of the primary requirements for organizations to abide by is to ensure that an ELD is properly installed in all commercial motor vehicles used for interstate operations. The FMCSA requires carriers to use ELDs to track and store driver’s hours-of-service data electronically, in order to ensure compliance with hours-of-service regulations.
Carriers must also comply with the FMCSA’s ELD requirements in order to be eligible for ELD certification. This includes implementation of an active and functioning ELD system as well as training of drivers on how to use the system correctly. Furthermore, carriers must be able to monitor and verify the accuracy of their drivers’ hours-of-service data in order to comply with FMCSA regulations.
To make sure that carriers are adhering to all ELD regulations, the FMCSA conducts inspections of carriers as part of its Compliance, Safety, Accountability (CSA) program. During these inspections, investigators will review the carrier’s ELD system to ensure accuracy and proper implementation. Furthermore, carriers may be subject to roadside inspections which include reviews of driver logs to check for compliance with hours-of-service regulations.
By following FMCSA guidelines and ensuring that all necessary components of an ELD system are in place, carriers can comply with the ELD mandate and avoid any potential penalties or violations. Carriers should also make sure that their drivers are regularly trained on how to use the system correctly, as this will help ensure accuracy in driver logs and compliance with regulations. With proper implementation and maintenance of an ELD system, carriers can ensure they are in compliance with the ELD mandate and avoid any potential penalties or violations. This will also ensure greater safety for drivers and improved efficiency of operations.
Who is exempt from the ELD mandate?
The ELD Mandate affects most motor carriers and drivers who operate commercial motor vehicles, but there are some exceptions.
Drivers and motor carriers operating vehicles that are not required to have a commercial driver’s license (CDL) under 49 CFR 383, do not need to comply with the mandate. In addition, drivers using paper RODS for not more than 8 days out of every 30-day period and drivers who only operate vehicles manufactured before 2000 are exempt from the ELD Mandate.
Drivers that use the 100 air-mile radius exemption or those operating under a “short-haul” exception also do not need to comply with the mandate. Motor carriers should consult the FMCSA’s ELD Mandate Exemption Fact Sheet for more information.
It is important to note that even if a driver or motor carrier is exempt from the mandate, they may still use an ELD in their vehicles. Additionally, drivers and carriers who are exempt may need to maintain records of duty status using paper RODS or an ELD, depending on the type of exemption.
Motor carriers should contact their state’s department of motor vehicles to determine which rules and regulations apply to them, and are encouraged to consult with legal counsel to ensure they are in compliance with any applicable laws or regulations.
Advantages of the ELD Mandate
The ELD Mandate provides numerous advantages for the trucking industry. For example, it helps to save time and money through greater efficiency on the roads. By eliminating unnecessary paperwork, drivers no longer have to spend hours of their day filling out logs.
Furthermore, this mandate increases safety on the road by preventing driver fatigue. With an ELD in place, drivers are no longer able to ignore hours of service regulations that make sure they take regular breaks and rest periods.
The mandate has also improved data accuracy and allows real-time tracking of hours. This enables companies to easily monitor their employees’ activity and ensure compliance with federal regulations.
All in all, the ELD Mandate has been instrumental in improving the overall safety and efficiency of the trucking industry.
Electronic Logging Device Technology and Training
ELD technology is a fast-growing sector of the trucking and transportation industry, offering improved efficiency and compliance for fleets. Because they are now mandatory across the trucking industry, fleets must be properly trained to use the technology.
ELD training is critical for compliance with DOT regulations, as well as to ensure accurate data collection and efficient operations. Companies that invest in proper training can eliminate errors and maximize the benefits of their ELD systems.
Training should cover installation and use of the ELD, as well as more complex topics such as setting up driver profiles, entering data correctly, troubleshooting issues, and understanding HOS regulations.
Companies should ensure that their personnel are adequately trained on ELDs before implementing them in their operations. Additionally, companies should regularly review procedures with drivers to ensure accuracy and compliance.
By investing in regular ELD training, a company can ensure that its drivers are properly equipped to handle the complexities of using the technology. Consistent review of procedures with drivers is key to ensuring that data is accurately entered and that HOS regulations are followed.
Additional Resources
The FMCSA offers resources to help drivers understand and comply with the ELD mandate. These include tutorials, webinars, and other information about the regulations and requirements for using an ELD. Additionally, the agency has created an ELD website that provides all necessary information on how to install, use, maintain, and troubleshoot compliant devices.
Drivers can find a list of certified ELD providers on the website, as well as links to other useful resources. Finally, the FMCSA has released an FAQ document that addresses common questions about the ELD mandate and its implementation. This document is a valuable resource for drivers who are still learning about the rule.
Conclusion
Ultimately, ELDs offer immense opportunities for improved operations and safety outcomes within the trucking industry. The ELD mandate is an important step in improving safety on the roads. Carriers that are ELD compliant will avoid costly fines, and benefit from improved operational efficiency and improved road safety.
If you need help to become ELD compliant, please don’t hesitate to reach out and schedule a call.